(Food)维生素D和紫外线
关键信息
紫外线 UVA, UVB
Note
- UVB 无法穿透玻璃,可产生维生素D,同时也是晒黑、皮肤癌风险的因素;
- UVA 可穿透玻璃,是皮肤老化皱纹的主要因素,不可产生维生素D。
| Aspect | UVA | UVB |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength Range | 320-400 nm | 280-320 nm |
| Penetration to Glass | Can penetrate through glass | Mostly blocked by glass |
| Penetration in Skin | Reaches dermis (second layer) | Affects epidermis (outer layer) |
| Tanning | Causes immediate tanning (lasting shorter) | Causes delayed tanning (lasting longer) |
| Sunburn | Minimal contribution to sunburn | Major cause of sunburn |
| Skin Aging | Major contributor to skin aging and wrinkles (photoaging) | Minimal contribution compared to UVA |
| Cancer Risk | Contributes to some skin cancers | Major cause of most skin cancers |
| Vitamin D Production | Does not help in producing vitamin D | Essential for vitamin D production |
概述
相关概念
- Cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3): This is a type of vitamin D that your skin produces when exposed to sunlight. It is also found in some foods and supplements. Vitamin D3 is converted in the liver to Calcidiol.
胆钙化醇(维生素 D3):这是皮肤在暴露在阳光下时产生的一种维生素 D。它也存在于一些食物和补充剂中。维生素 D3 在肝脏中转化为骨化二醇。 - Ergocalciferol (Vitamin D2): This is another form of vitamin D, found in some plants and fungi. It is similar to Vitamin D3, but not as effective in raising vitamin D levels in the blood.
麦角钙化醇(维生素 D2):这是维生素 D 的另一种形式,存在于一些植物和真菌中。它与维生素 D3 相似,但在提高血液中的维生素 D 水平方面效果不佳。 - Calcidiol (25-Hydroxyvitamin D): Also known as 25(OH)D, this is the form of vitamin D that circulates in the blood. It is produced in the liver from Vitamin D3 and D2. Calcidiol is used to measure a person’s vitamin D status.
骨化二醇(25-羟基维生素 D):也称为 25(OH)D,这是在血液中循环的维生素 D 的形式。它是在肝脏中由维生素 D3 和 D2 产生的。骨化二醇用于测量一个人的维生素 D 状况。 - Calcitriol (1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D): Also know as D 1,25(OH)2D. This is the active form of vitamin D, produced in the kidneys from Calcidiol. Calcitriol is responsible for most of the biological actions of vitamin D, such as calcium absorption and bone health.
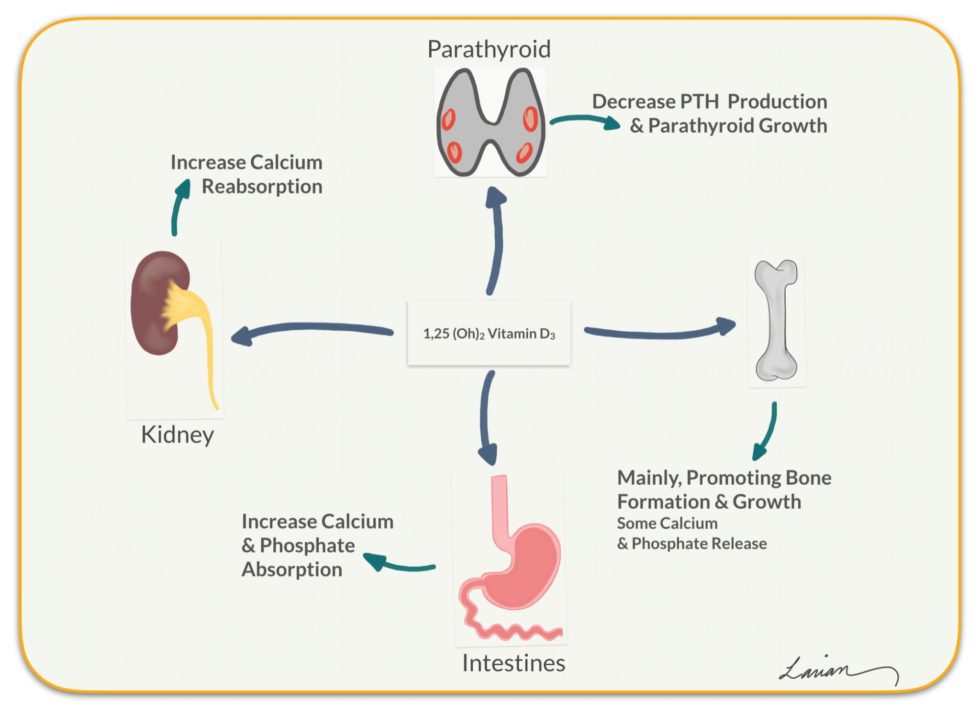
骨化三醇(1,25-二羟基维生素 D):这是维生素 D 的活性形式,由骨化二醇在肾脏中产生。骨化三醇负责维生素 D 的大部分生物作用,例如钙吸收和骨骼健康。
活性维生素D是骨化三醇(Calcitriol),骨化三醇促使小肠壁细胞产生更多的钙结合蛋白(calbindin-D proteins),增加钙在小肠的吸收。当维生素D不足,小肠吸收钙的比例只有10%-15%,但当维生素D充足,小肠钙吸收率可以提高到30%-40%,[4]
The overall pathway is:
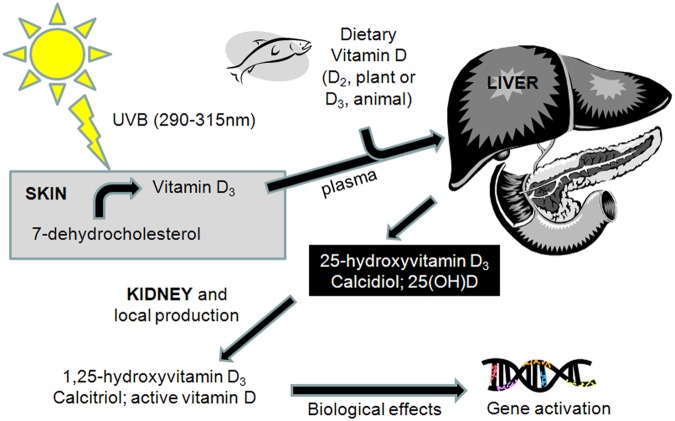
- Cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3) or Ergocalciferol (Vitamin D2) -> Calcidiol (25-Hydroxyvitamin D) in the liver.
皮肤晒太阳产生D3、食物中的D2/D3在肝脏中转化为骨化二醇。 - Calcidiol -> Calcitriol (1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D) in the kidneys.
骨化二醇在肾脏中转化为骨化三醇。
维生素 D 对运动健康的益处 - PMC --- Sports Health Benefits of Vitamin D - PMC
来源
剂量
RDA / AI
- 推荐膳食摄入量(RDA, Recommended Dietary Allowance):满足几乎所有(97%-98%)健康个体的营养需求的平均每日摄入水平;常用于为个体规划营养充足的饮食
- 充足摄入量(AI, Adequate Intake):此水平的摄入被认为可以确保营养充足;在证据不足以制定 RDA 的情况下设立
维生素D 推荐膳食摄入量
- 成年男性/女性/妊娠 RDA:15 mcg = 600 IU
- 老人 RDA: ** 20 mcg = 800 IU **
Table 2: Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) for Vitamin D [1]
| Age | Male | Female | Pregnancy | Lactation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-12 months* (AI) | 10 mcg (400 IU) |
10 mcg (400 IU) |
||
| 1–13 years | 15 mcg (600 IU) |
15 mcg (600 IU) |
||
| 14–18 years | 15 mcg (600 IU) |
15 mcg (600 IU) |
15 mcg (600 IU) |
15 mcg (600 IU) |
| 19–50 years | 15 mcg (600 IU) |
15 mcg (600 IU) |
15 mcg (600 IU) |
15 mcg (600 IU) |
| 51–70 years | 15 mcg (600 IU) |
15 mcg (600 IU) |
||
| >70 years | 20 mcg (800 IU) |
20 mcg (800 IU) |
UL (Tolerable Upper Intake Level )
- 可耐受最高摄入量(UL):不太可能导致不良健康影响的最大每日摄入量
维生素D UL
- 成人、老人、妊娠、哺乳 UL:100 mcg (4,000 IU)
Table 4: Tolerable Upper Intake Levels (ULs) for Vitamin D [1]
| Age | Male | Female | Pregnancy | Lactation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–6 months | 25 mcg (1,000 IU) | 25 mcg (1,000 IU) | ||
| 7–12 months | 38 mcg (1,500 IU) | 38 mcg (1,500 IU) | ||
| 1–3 years | 63 mcg (2,500 IU) | 63 mcg (2,500 IU) | ||
| 4–8 years | 75 mcg (3,000 IU) | 75 mcg (3,000 IU) | ||
| 9–18 years | 100 mcg (4,000 IU) | 100 mcg (4,000 IU) | 100 mcg (4,000 IU) | 100 mcg (4,000 IU) |
| 19+ years | 100 mcg (4,000 IU) | 100 mcg (4,000 IU) | 100 mcg (4,000 IU) | 100 mcg (4,000 IU) |
单位换算
维生素D单位
- Vitamin D 1 mcg = 40 IU, 微克mcg✖40 = IU
- 25mcg = 1000 IU
- 1 nmol/L = 0.4 ng/mL, 1 ng/mL = 2.5 nmol/L,ng✖2.5 = nmol
- 20ng/ml = 50nmol/L
水平
- 足够:> 50 nmol/L (20 ng/mL)
- 过低:< 30 nmol/L (12 ng/mL)
- 过高:> 125 nmol/L (50 ng/mL)
其他
参考文献
- Vitamin D - Health Professional Fact Sheet, Updated: July 26, 2024